| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
- programming
- 함수
- 티스토리챌린지
- pass by reference
- Python
- 백준
- 알고리즘
- Pre-processing
- Class
- function
- vscode
- 문자열
- Deep Learning
- string
- const
- OOP
- raw data
- pointer
- 반복문
- assignment operator
- baekjoon
- 파이썬
- C++
- 오블완
- array
- 배열
- predictive analysis
- 포인터
- Object Oriented Programming
- Data Science
- Today
- Total
Channi Studies
[Data Structure] Circular Queue (ADT) 본문
[Data Structure] Circular Queue (ADT)
Chan Lee 2025. 4. 2. 12:02Circular Queue
A queue is an ADT in which items are inserted at the end of the queue and removed from the front of the queue.
The queue enqueue oepration inserts an item at the end of the queue.
The queue dequeue operation removes and returns the item at the front of the queue.
A queue is reffered to as a first-in first-out (FIFO) ADT.
Remembering queue = FIFO and stack = LIFO can make your life easier.
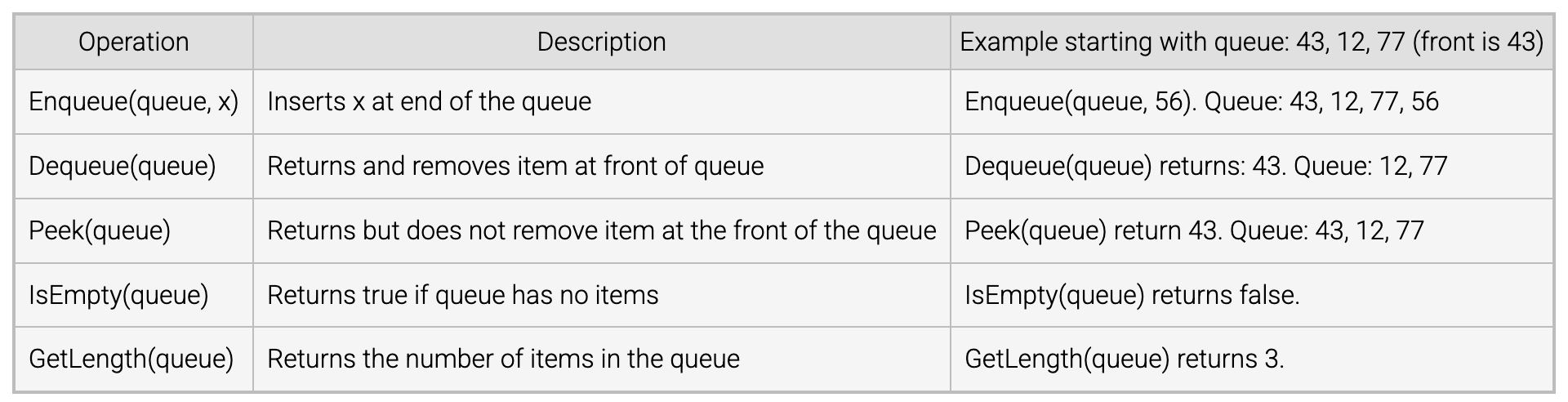
Basically, the implementation of queue is very intuitive and is a slight variation of that of stack.
If we use linked list data type for Queue ADT:
- If the head pointer is null, the queue is empty
- If we Enqueue an item, the tail node's next pointer changes.
- If we Dequeue an item, the head node changes.
Python: Array-Based Queue
Array-Based Queue is a queue implemented using an array data type.
Two variables are required in addition to the array:
- length: an integer for the queue's length.
- front_index: an integer for the queue's front item index.
This image will help your understanding on the meaning of front_index variable.

Similar to the Stack, we can either choose the queue to be bounded or unbounded, by introducing an additional object variable max_length.
A bounded queue (or a bounded stack) with a length equal to the maximum length is said to be full.
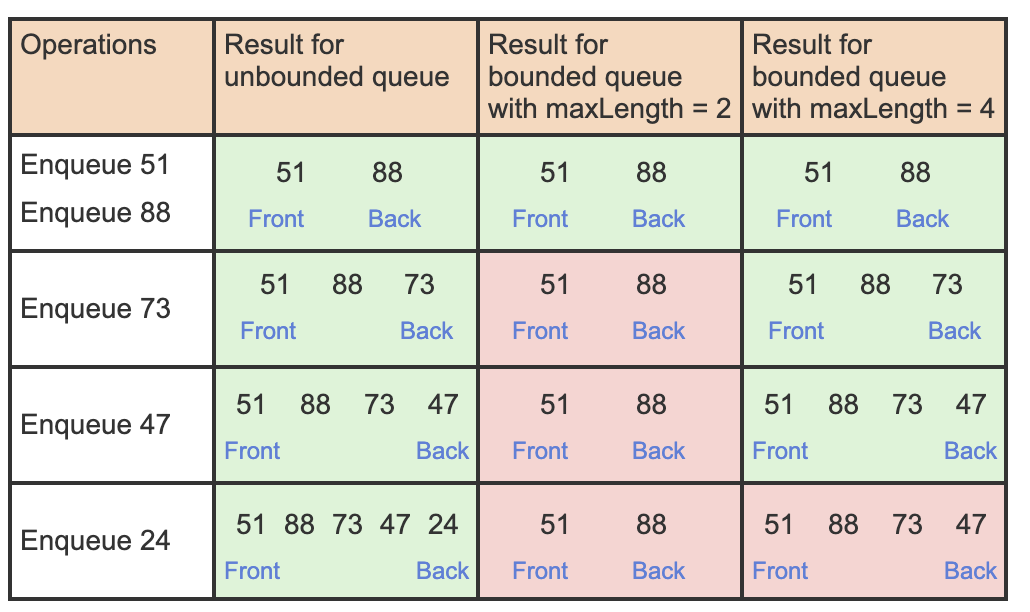
Again, similar to Stack we can use a flexible approach by using max_length for both bounded and unbounded queues, but differentiate based on its sign.
Negative max_length will tell that the queue is unbounded, so we will set the default value as -1 for max_length.
Next, we will take a look into resize algorithm that's needed when we are tyring to Enqueue when length = max_length.
def resize(self):
new_size = len(self.queue_list) * 2
if self.max_length >= 0 and new_size > self.max_length:
new_size = max_length
new_list = [0] * new_size
for i in range(self.length):
item_index = (self.front_index + i) % len(self.queue_list)
new_list[i] = self.queue_list[item_index]
self.queue_list = new_list
self.front_index = 0
enqueue and dequeue methods are as following:
def enqueue(self, item):
if self.length == self.max_length:
return False
if self.length == len(self.queue_list):
self.resize()
item_index = (self.front_index + self.length) % len(self.queue_list)
self.queue_list[item_index] = item
self.length += 1
return True
def dequeue(self):
to_return = self.queue_list[self.front_index]
self.length -= 1
self.front_index = (self.front_index + 1) % len(self.queue_list)
return to_return'Data Science > Data Structure & Algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Data Structure] Hash Table - 1 | Basic Operations & Chaining Collision Handling Technique (0) | 2025.04.09 |
|---|---|
| [Data Structure] Deque (ADT) (0) | 2025.04.02 |
| [Data Structure] Stack (ADT) (0) | 2025.04.02 |
| [Data Structure] Array–Based Lists (ADT) (0) | 2025.03.28 |
| [Data Structure] Doubly-Linked Lists (0) | 2025.03.28 |




