| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 | 31 |
- 파이썬
- Python
- 티스토리챌린지
- Deep Learning
- OOP
- 백준
- 배열
- function
- Data Science
- C++
- 오블완
- Pre-processing
- baekjoon
- assignment operator
- 함수
- Class
- string
- 알고리즘
- programming
- 문자열
- pass by reference
- const
- Object Oriented Programming
- array
- raw data
- vscode
- 포인터
- predictive analysis
- 반복문
- pointer
- Today
- Total
Channi Studies
[SQL] Day 1: Database and Table 본문
Database works like a folder, and table works like a file in SQL.
We will work in the query window of MySQL Workbench Software, that can be accessed after succesfully connecting to MySQL server.
Database
To create a database, we use CREATE query
(MySQL is not case-sensitive, meaning that you can use either CREATE, Create, create, CrEaTe, etc)
CREATE DATABASE myDB;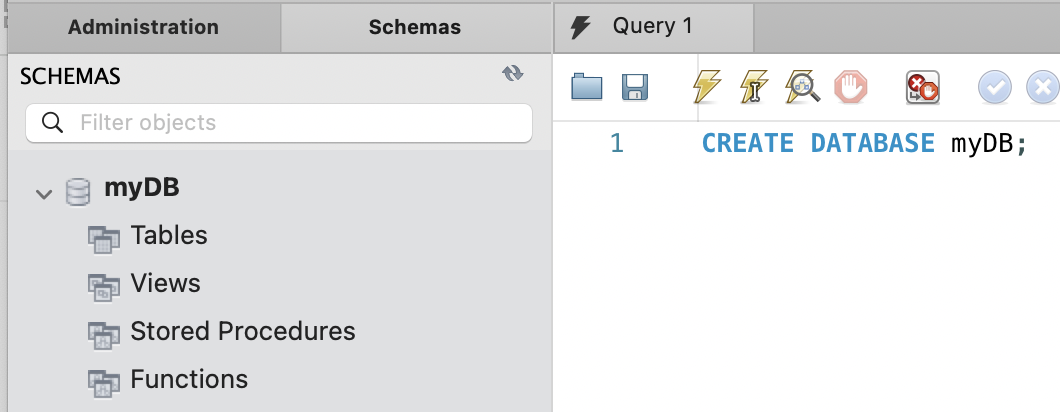
To use the created database, you can either (1) right click the database and click 'Set as Default Schema' or (2) use following statement:
USE myDB;
To drop (remove) the database, you can use DROP query:
DROP DATABASE myDB;
To set a database to read only, you can use ALTER query:
ALTER DATABASE myDB READ ONLY = 1;If a database is in read only mode, we can't modify the data, but we can still access the data within.
If you want to remove read only option,
ALTER DATABASE myDB READ ONLY = 0;
Any attempt to modify the database will fail as following:

Table
Tables in SQL consists of rows and colums, like excel spreadsheets.
We will focus on creating a table and basic modification on the columns.
To create a table, you will need to write CREATE TABLE table_name();
CREATE TABLE employees(
employee_id INT,
first_name VARCHAR(50),
last_name VARCHAR(50),
hourly_pay DECIMAL(5, 2),
hire_date DATE
);Each line, there is name of the column followed by the type of the stored data.
INT: integer
VARCHAR(n): Series of characters with limit of n
DECIMAL(a, b): A decimal with (a = maximum number of digits; b = precision)
DATE: date
executing the script will give (Check the columns):

If you need to select a table, you will need to use SELECT query:
SELECT * from employees;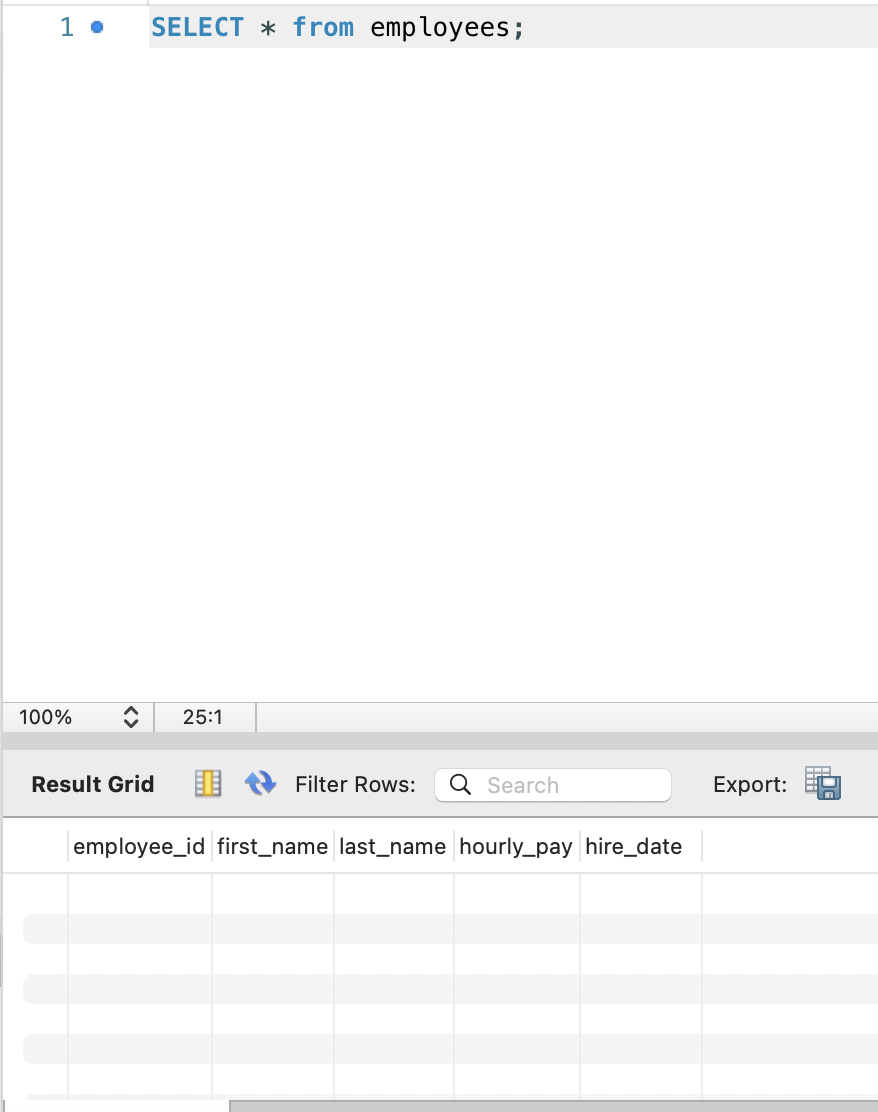
You can rename a table using RENAME quiery
RENAME TABLE employees TO workers;
Dropping a table would be the same as dropping a database:
DROP TABLE employees;
If you need to alter a table, there is the ALTER keyword.
Say that we're adding phone_number column to employees table.
ALTER TABLE employees
ADD phone_number VARCHAR(15);
SELECT * from employees;
Renaming a column would also use ALTER keyword, with RENAME:
ALTER TABLE employee
RENAME COLUMN phone_number TO email;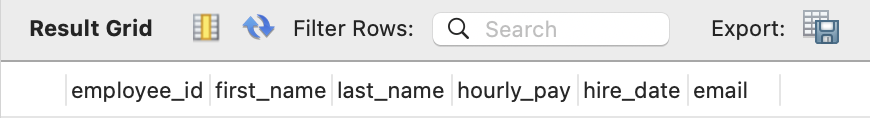
However, email might require longer data type.
To change the data type of a column, we again use ALTER keyword, with MODIFY this time.
ALTER TABLE employees
MODIFY COLUMN email VARCHAR(100);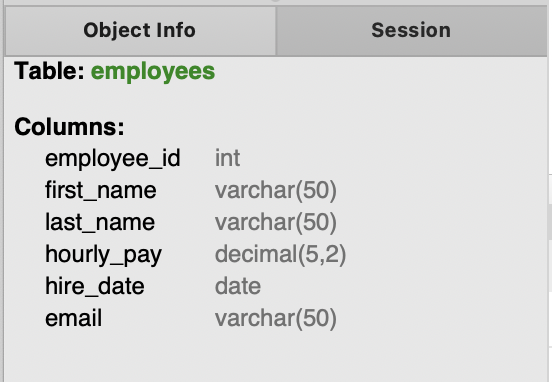
Maybe we need to reposition some column.
Let's move email column next to the last_name column.
ALTER TABLE employees
MODIFY email VARCHAR(100)
AFTER last_name;
SELECT * from employees;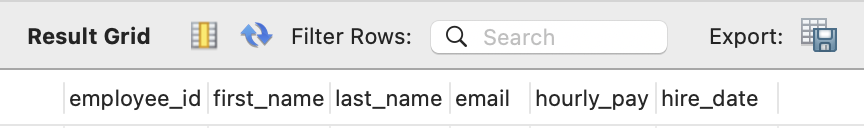
If you want the column to be at first, you can simply write FIRST instead of AFTER last_name.
'SQL' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [MySQL] Day 5. CURRENT_DATE() & CURRENT_TIME() (0) | 2025.03.28 |
|---|---|
| [MySQL] Day 4. AUTOCOMMIT, COMMIT, ROLLBACK (0) | 2025.03.26 |
| [MySQL] Day 3. Update and Delete (0) | 2025.03.25 |
| [SQL] Day 2: INSERT INTO & SELECT WHERE (0) | 2025.03.15 |
| [SQL] Day 0: Setup (0) | 2025.03.14 |




