| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 | 31 |
- 배열
- Object Oriented Programming
- baekjoon
- Pre-processing
- string
- 반복문
- 백준
- function
- assignment operator
- Python
- array
- C++
- 문자열
- 알고리즘
- pass by reference
- 포인터
- raw data
- programming
- vscode
- Class
- 파이썬
- 함수
- Data Science
- 티스토리챌린지
- predictive analysis
- pointer
- 오블완
- const
- OOP
- Deep Learning
- Today
- Total
Channi Studies
[Data Structure] Graphs: Intro, Adjacency Lists, Adjacency Matrices 본문
[Data Structure] Graphs: Intro, Adjacency Lists, Adjacency Matrices
Chan Lee 2025. 5. 26. 08:47Graphs
A graph is a data structure for representing connections among items, and consists of vertices connected by edges.
- A vertex (or node) represents an item in a graph.
- An edge represents a connection between two vertices in a graph.
In a graph,
- Two vertices are adjacent if connected by an edge.
- A path is a sequence of edges leading form a source vertex to a destination vertex. The path length is the number of edges in the path.
- The distance between two vertices is the number of edges on the shortest path between those vertices.

우리는 각 노드를 연결하는 edge의 길이, 색 또는 다양한 값을 통해서 weight (가중치)를 부여할 수 있습니다.
예를 들면 지도 프로그램에서 각 목적지 vertex 까지의 거리 edge를 이동 시간과 비례하여 증가하게 만들 수 있겠습니다.
Adjacency Lists
Graph data structure를 다룰 때에는 다양한 접근이 있습니다.
그 중 하나는 adjacency list 를 사용하는 것 입니다.
Recall that two vertices are adjacent if connected by an edge.
In an adjacency list graph representation, each vertex has a list of adjacent vertices, each list item representing an edge.
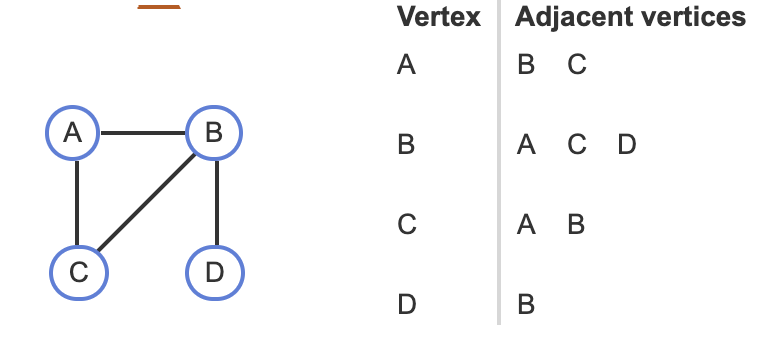
A key advantage of an adjacency list graph representation is a sized of O(V + E) where V refers to the number of vertices and E the number of edges.
A distadvantage is that determining whether two vertices are adjacent is O(V), because one vertex's adjacency list must be traversed looking for the other vertex, and that list could have V items.
However, in most applications, a vertex is only adjacent to a small fraction of the other vertices, yielding a sparse graph, which is a graph having a far fewer edges than the maximum possible.
Adjacency Matrices
Another approach is an adjacency matrix.
In an adjacency matrix, each vertex is assigned to a matrix row and column, and a matrix element is 1 if the corrsponding two vertices have an edge (adjacent) or is 0 otherwise.
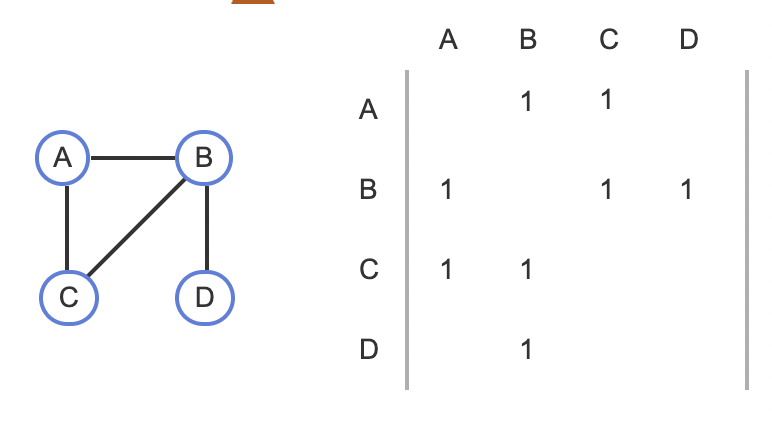
Assuming the common implementation as a two-dimensional array whose elements are accessible in O(1), then an adjacency matrix's key benefit is O(1) determination of whether two vertices are adjacent: The corresponding element is just checked for 0 or 1.
A key drawback is O(V²) size. Ex: A graph with 1000 vertices would require a 1000 x 1000 matrix, meaning 1,000,000 elements. An adjacency matrix's large size is inefficient for a sparse graph, in which most elements would be 0's.
An adjacency matrix only represents edges among vertices; if each vertex has data, like a person's name and address, then a separate list of vertices is needed.
'Data Science > Data Structure & Algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Data Structure] Directed Graphs (0) | 2025.05.26 |
|---|---|
| [Data Structure] Graphs: Breadth-first Search / Depth-first Search (0) | 2025.05.26 |
| [ADT] Set - 3 | Python Implementation (0) | 2025.05.15 |
| [ADT] Set - 2 | Set Opeartions (0) | 2025.05.15 |
| [ADT] Set - 1 (0) | 2025.05.15 |



