| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 | 31 |
- pass by reference
- programming
- 배열
- 포인터
- pointer
- raw data
- C++
- 반복문
- Object Oriented Programming
- 티스토리챌린지
- Pre-processing
- 파이썬
- 백준
- 함수
- array
- baekjoon
- Data Science
- assignment operator
- Deep Learning
- const
- function
- string
- 문자열
- predictive analysis
- Class
- 오블완
- Python
- OOP
- 알고리즘
- vscode
- Today
- Total
Channi Studies
[Data Structure] Graphs: Breadth-first Search / Depth-first Search 본문
[Data Structure] Graphs: Breadth-first Search / Depth-first Search
Chan Lee 2025. 5. 26. 13:57Breadth-First Search
An algorithm commonlyu must visit every vertex in a graph in some order, known as a graph traversal.
A breadth-first search (BFS) is a traversal that visits a starting vertex, then all vertices of distance 1 from that vertex, then of distance 2, and so on, without revisiting a vertex.

Since the visiting order of same-distance vertices doesn't matter, there can be multiple graph traversals if we use BFS method.
Breadth-first search algorithm
BFS(startV) {
Enqueue startV in frontierQueue
Add startV to discoveredSet
while ( frontierQueue is not empty ) {
currentV = Dequeue from frontierQueue
"Visit" currentV
for each vertex adjV adjacent to currentV {
if ( adjV is not in discoveredSet ) {
Enqueue adjV in frontierQueue
Add adjV to discoveredSet
}
}
}
}When the BFS algorithm first encounters a vertex, that vertex is said to have been discovered.
In the BFS algorithm, the vertices in the queue are called the frontier, being vertices thus far discovered but not yet visited. Because each vertex is visited at most once, an already-discovered vertex is not enqueued again.
A "visit" may mean to print the vertex, append the vertex to a list, compare vertex data to a value and return the vertex if found, etc.
Depth-First Search
A depth-first search (DFS) is a traversal that visits a starting vertex, then visits every vertex along each path starting from that vertex to the path's end before backtracking.
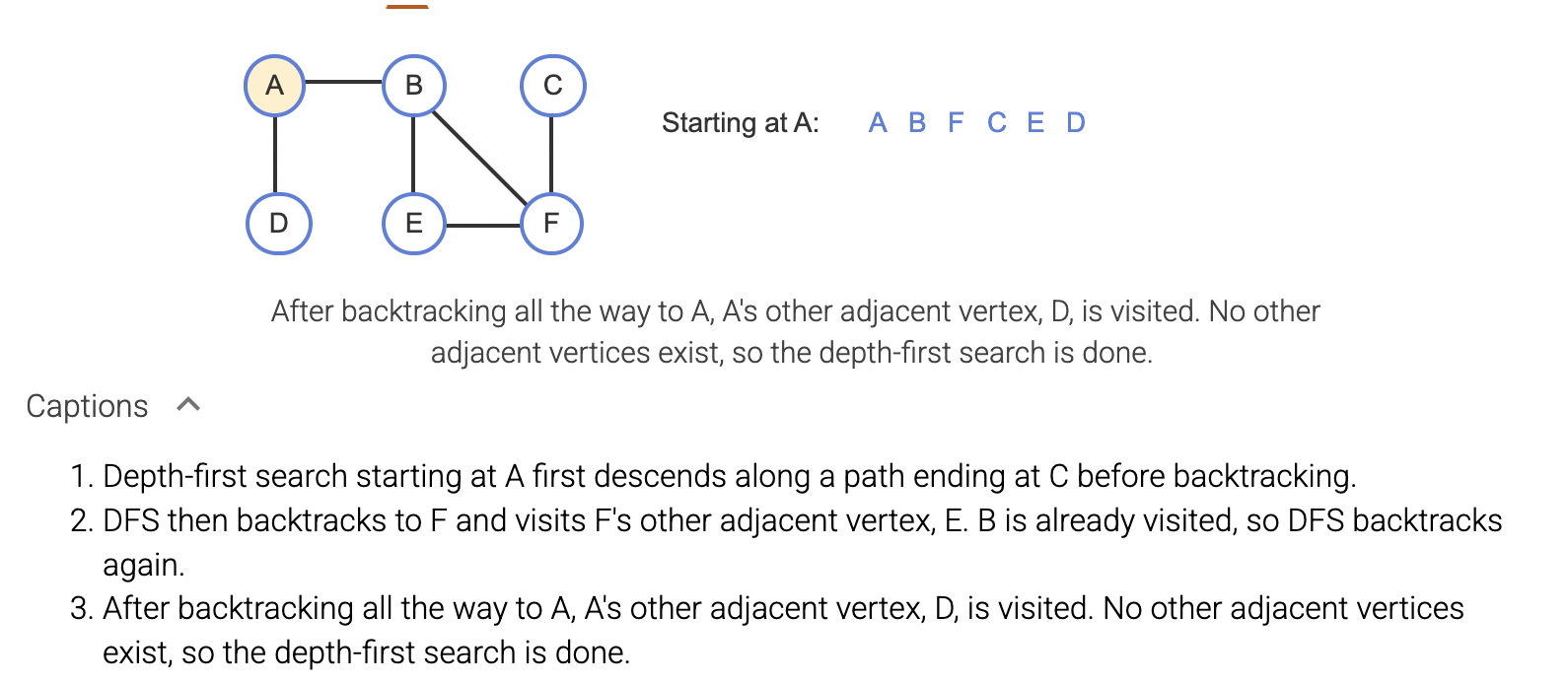
Same as the BFS, DFS traversal can also have multiple traversal paths.
DFS Algorithm
DFS(startVertex) {
Create new, empty stack named vertexStack
Create new, empty set named visitedSet
Push startVertex to vertexStack
while (vertexStack is not empty) {
currentV = Pop vertexStack
if (currentV is not in visitedSet) {
Visit currentV
Add currentV to visitedSet
for each vertex adjV adjacent to currentV {
Push adjV to vertexStack
}
}
}
}
Recursive DFS Algorithm
RecursiveDFS(currentV) {
if ( currentV is not in visitedSet ) {
Add currentV to visitedSet
"Visit" currentV
for each vertex adjV adjacent to currentV {
RecursiveDFS(adjV)
}
}
}
'Data Science > Data Structure & Algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Data Structure] Weighted Graphs (0) | 2025.05.26 |
|---|---|
| [Data Structure] Directed Graphs (0) | 2025.05.26 |
| [Data Structure] Graphs: Intro, Adjacency Lists, Adjacency Matrices (0) | 2025.05.26 |
| [ADT] Set - 3 | Python Implementation (0) | 2025.05.15 |
| [ADT] Set - 2 | Set Opeartions (0) | 2025.05.15 |



