| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
- 오블완
- 포인터
- pass by reference
- 문자열
- 함수
- string
- 티스토리챌린지
- C++
- const
- Pre-processing
- Class
- function
- 알고리즘
- assignment operator
- 백준
- programming
- Object Oriented Programming
- 파이썬
- array
- pointer
- vscode
- Data Science
- raw data
- predictive analysis
- Deep Learning
- Python
- 반복문
- 배열
- OOP
- baekjoon
- Today
- Total
Channi Studies
[MySQL] Day 13. FUNCTIONS 본문
A function is a stored program that you can pass a parameters into to return a value.
There are lots of functions offered by MySQL that can be found in following reference manual.
MySQL :: MySQL 8.4 Reference Manual :: 14.1 Built-In Function and Operator Reference
14.1 Built-In Function and Operator Reference The following table lists each built-in (native) function and operator and provides a short description of each one. For a table listing functions that are loadable at runtime, see Section 14.2, “Loadable F
dev.mysql.com
We will take a look into few useful functions from all those.
1. COUNT( )
The COUNT() function returns the number of rows that matches a specific criterion.
Consider following transactions table.

We can see that there are 5 rows in the table currently.
We can count the total number of rows by:
-- SELECT COUNT(column_name)
-- FROM table_name
-- WHERE condition;
SELECT COUNT(amount)
FROM transactions;
Let's check how many rows are there for customer_id = 3
SELECT COUNT(amount)
FROM transactions
WHERE customer_id = 3;
It matches our expectation.
Now, this is not necessary step but COUNT(amount) is not a very great name.
We can actually rename those COUNT columns by using AS keyword with custom string.
SELECT COUNT(amount) AS "# of rows"
FROM transactions;
Or simply like this
SELECT COUNT(amount) AS count
FROM transactions;
2. MIN( ) and MAX( )
The MIN() and MAX()function returns the smallest and the largest value of the selected column, respectively.
SELECT MIN(amount) AS "Smallest Transaction"
FROM transactions;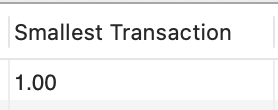
SELECT MAX(amount) AS "Maximum Transaction"
FROM transactions;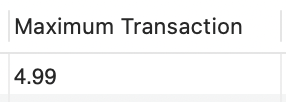
3. AVG( )
The AVG() function returns the average value of the column.
SELECT AVG(amount) AS "Average Transaction Amount"
FROM transactions;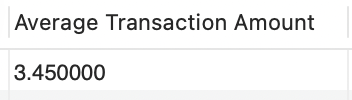
4. SUM( )
The SUM() function returns the sum of the all values of the column.
SELECT SUM(amount) AS "Total Transaction Amount"
FROM transactions;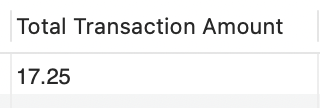
5. CONCAT( )
The CONCAT() string function adds two or more expressions together.
-- Syntax: CONCAT(expression1, expression2, expression3,...)
SELECT CONCAT(first_name, " ", last_name) AS "Full Name"
FROM employees;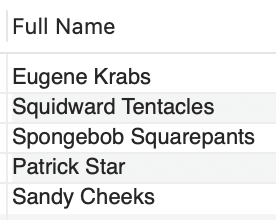
There are numerous useful functions available for MySQL, but these are some basic functions that are useful to beginners!
'SQL' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [MySQL] Day 14. Logical Operators (AND, OR, NOT, BETWEEN, IN) (0) | 2025.04.22 |
|---|---|
| [MySQL] Day 12. JOINS (INNER JOIN, LEFT JOIN, RIGHT JOIN) (0) | 2025.04.09 |
| [MySQL] Day 11. FOREIGN KEY constraint (0) | 2025.04.07 |
| [MySQL] Day 10. AUTO_INCREMENT attribute (0) | 2025.04.06 |
| [MySQL] Day 9. PRIMARY KEYS constraint (0) | 2025.04.06 |





