| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
- const
- 백준
- OOP
- predictive analysis
- 문자열
- programming
- 티스토리챌린지
- 포인터
- function
- C++
- string
- Deep Learning
- 오블완
- Object Oriented Programming
- baekjoon
- Python
- 알고리즘
- assignment operator
- 반복문
- pointer
- Data Science
- 함수
- Pre-processing
- array
- vscode
- pass by reference
- 배열
- Class
- raw data
- 파이썬
- Today
- Total
Channi Studies
[Data Structure] BST Inorder Traversal, Height, and Insertion Order 본문
[Data Structure] BST Inorder Traversal, Height, and Insertion Order
Chan Lee 2025. 4. 22. 04:57Binary Search Tree Inorder Travsersal
A tree traversal algorithm visits all nodes in the tree once and performs an operation on each node.
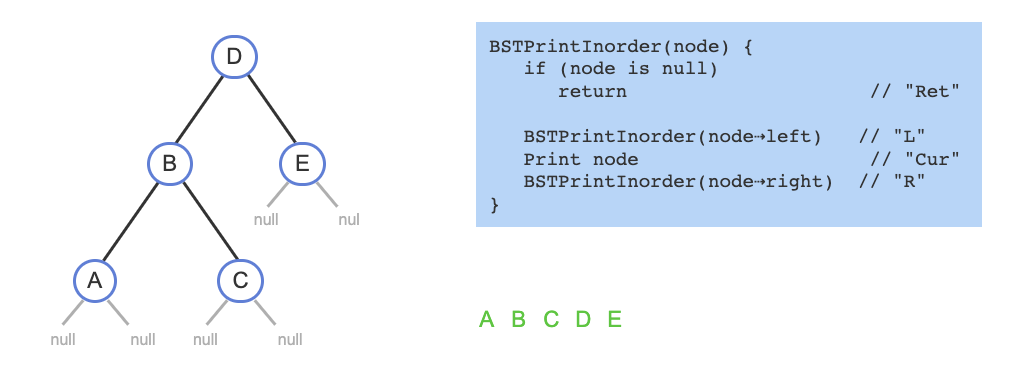
An inoreder traversal visits all nodes in a BST from smallest to largest, which is useful for example to print the tree's nodes in sorted order.
Starting from the root, the algorithm recursively prints the left subtree, the current node, and the right subtree.
// Inorder Traversal Print Pseudocode
BSTPrintInorder(node) {
if (node is null)
return
BSTPrintInorder(node⇢left)
Print node
BSTPrintInorder(node⇢right)
}
BST Height and Insertion Order
Recall that a tree's height is the maximum edges from the root to any leaf. (Thus, a one-node tree has height 0.)
The minimum N-node binary tree height is h=⌊log2N⌋ (가우스 기호), achieved when each level is full except possibly the last.
The maximum N-node binary tree height is N - 1 (the - 1 is because the root is at height 0).
Searching a BST is fast if the tree's height is near the minimum. Inserting items in random order naturally keeps a BST's height near the minimum. In contrast, inserting items in nearly-sorted order leads to a nearly-maximum tree height.

BST GetHeight Algorithm
Given a node representing a BST subtree, the height can be computed as follows:
- If the node is null, return -1.
- Otherwise recursively compute the left and right child subtree heights, and return 1 plus the greater of the 2 child subtrees' heights.
// Pseudocode
BSTGetHeight(node) {
if (node is null) {
return -1
}
leftHeight = BSTGetHeight(node⇢left)
rightHeight = BSTGetHeight(node⇢right)
return 1 + max(leftHeight, rightHeight)
}
BST Getheight algorithm will have the worst runtime complexity of O(N).
'Data Science > Data Structure & Algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Data Structure] Python: Binary Search Tree (0) | 2025.04.23 |
|---|---|
| [Data Structure] BST Parent Node Pointers, and Recursion (0) | 2025.04.23 |
| [Data Structure] BST Operations - Search, Insert, and Remove (0) | 2025.04.22 |
| [Data Structure] Binary Search Trees (0) | 2025.04.22 |
| [Data Structures] Binary Tree - 2 | Application of Trees (File Systems, BSP) (0) | 2025.04.22 |


