| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
- Pre-processing
- 포인터
- string
- 알고리즘
- 문자열
- 함수
- 반복문
- Data Science
- 배열
- pointer
- pass by reference
- raw data
- vscode
- 백준
- Deep Learning
- Class
- const
- 오블완
- C++
- OOP
- predictive analysis
- programming
- 티스토리챌린지
- Python
- Object Oriented Programming
- baekjoon
- function
- 파이썬
- assignment operator
- array
- Today
- Total
Channi Studies
[Data Structure] AVL Tree - 1: Introduction 본문
[Data Structure] AVL Tree - 1: Introduction
Chan Lee 2025. 5. 1. 03:15AVL Tree
W3Schools.com
W3Schools offers free online tutorials, references and exercises in all the major languages of the web. Covering popular subjects like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, Python, SQL, Java, and many, many more.
www.w3schools.com
An AVL tree is a BST with a height balance property and specific operations to rebalance the tree when a node is inserted or removed.
A BST is height balanced if for any node, the heights of the node's left and right subtrees differ by only 0 or 1.
A node's balance factor is the left subtree height minus the right subtree height, which is 1, 0, or -1 in an AVL tree. For a non-existent left or right child's subtree's height is said to be -1.
Recall that a tree with just one node has height 0.
Don't forget that an AVL tree is still a BST, so the nodes must be structured in a sorted order.
항상 모든 가능한 subtree를 고려해야 합니다.
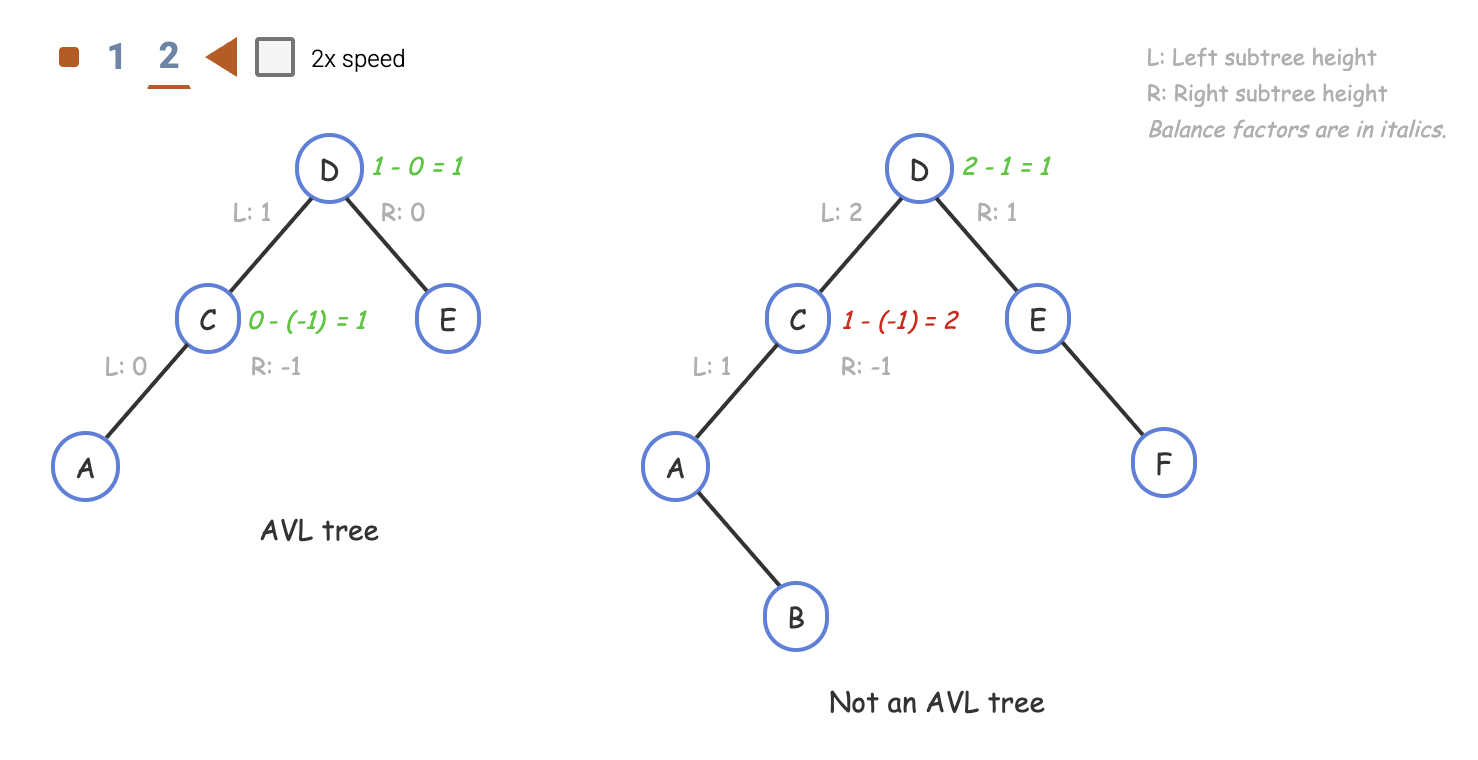
몇 가지 예시를 들어보겠습니다
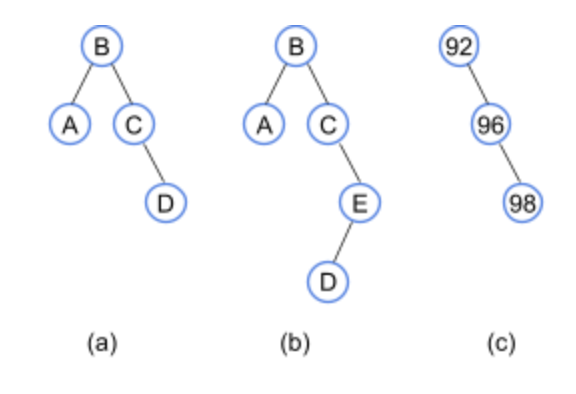
For (a), B's left subtree has height of 0 and right subtree has height of 1. C's left subtree has height of -1 and right subtree has height of 0. All of the balance factor differences are less or equal to 1. So it's an AVL tree.
For (b), B's left subtree has height of 0 and right subtree has height of 2. The difference is 2 > 1, so it's NOT an AVL tree.
For (c), 92's left subtree has height of -1 (non-existent) and right subtree has height of 1. The difference is 2 > 1, so it's NOT an AVL tree.
Height of AVL Tree
Minimizing binary tree height is key for efficient data structure and operations. We will discuss in more detail later.
AVL doesn't guarantee a minimum height, but theoreticians have shown that an AVL tree's worst case height is no worse than about 1.5 times the minimum binary tree height, so the height is still h = O(log N) where N is the number of nodes.
So for an AVL tree with 7 nodes, the minimum possible height will be h_min = O(log₂7) = 2.807 = 2
The maximum possible height will be h_max = 2 * 1.5 = 3
Storing Height at Each AVL Node
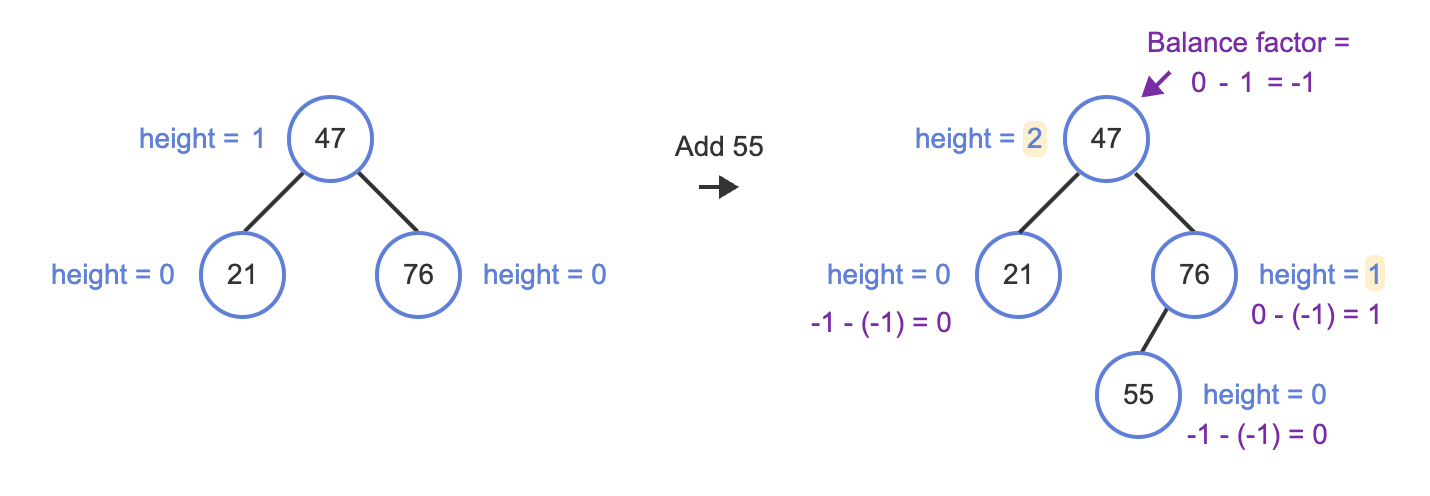
An AVL tree implementation can store the subtree height as a member of each node.
With the height stored as a member of each node, the balance factor can be computed in O(1) time.
When a node is inserted in or removed from an AVL tree, ancestor nodes may need the height value to be recomputed.
If a new node is inserted as a child of internal node with 1 child (for previously null-child's position), then the ancestors' height value don't have to be changed.
이름이 AVL Tree로 붙은 이유에 대해서 찾아보니 이 Self-balancing tree를 최초 고안한 수학자들의 이름을 딴 것이라고 합니다. The name of the inventors are Adelson-Velsky and Landis.
'Data Science > Data Structure & Algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Data Structure] AVL Tree - 3: AVL Insertions & Removals (0) | 2025.05.01 |
|---|---|
| [Data Structure] AVL Tree - 2: AVL Rotations (0) | 2025.05.01 |
| [Data Structure] Python: Binary Search Tree (0) | 2025.04.23 |
| [Data Structure] BST Parent Node Pointers, and Recursion (0) | 2025.04.23 |
| [Data Structure] BST Inorder Traversal, Height, and Insertion Order (0) | 2025.04.22 |


