| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
- baekjoon
- 포인터
- Deep Learning
- 배열
- const
- programming
- C++
- 문자열
- Class
- Object Oriented Programming
- raw data
- 알고리즘
- 파이썬
- Python
- Data Science
- 백준
- 반복문
- string
- array
- 오블완
- pointer
- OOP
- 함수
- 티스토리챌린지
- function
- predictive analysis
- pass by reference
- Pre-processing
- vscode
- assignment operator
- Today
- Total
Channi Studies
[Data Structure] AVL Tree - 2: AVL Rotations 본문
[Data Structure] AVL Tree - 2: AVL Rotations
Chan Lee 2025. 5. 1. 05:15Tree Rotation For Balancing
Inserting an item into an AVL tree may require rearranging the tree to maintain height balance.
A rotation is a local rearrangement of a BST that maintains the BST ordering property while rebalancing the tree.
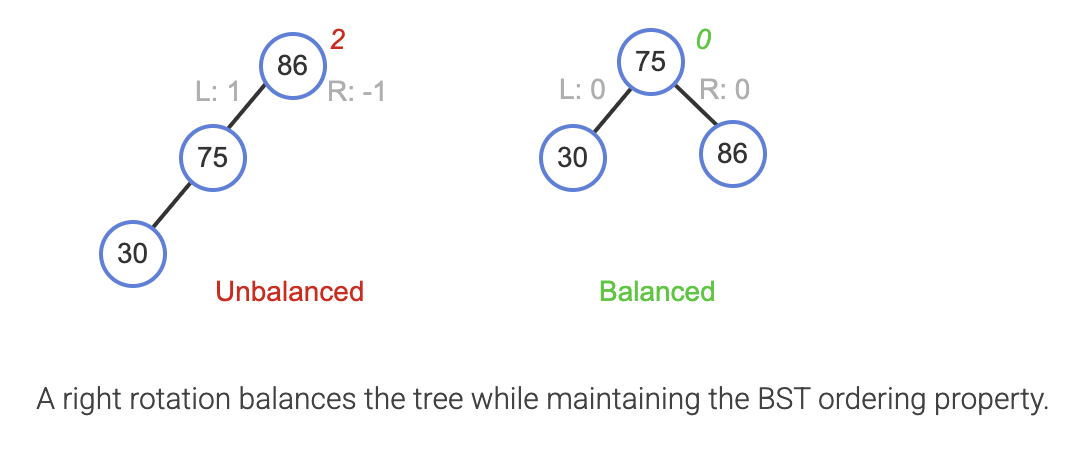
*Rotation is said to be done at a node. Ex. Above, the right rotation is done at node 86.
In the example above, if the node 75 had a right child, then the right child would've changed to 86's left child to maintain BST ordering property.

Obviously, we can also perform a left rotation with just opposite direction.
Before get to know about the detailed rotation algorithms, we should learn about the basic algorithms for AVL tree.
이 알고리즘들은 천천히 읽어보면 이해하기가 매우 쉽습니다.
조금만 시간을 들여서 읽으면 직관적으로 이해할 수 있습니다.
The AVLTreeUpdateHeight algorithm updates a node's height value by taking the maximum of the child subtree heights and adding 1.
AVLTreeUpdateHeight(node) {
leftHeight = -1
if (node→left != null)
leftHeight = node→left→height
rightHeight = -1
if (node→right != null)
rightHeight = node→right→height
node→height = max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1
}
The AVLTreeSetChild algorithm sets a node as the parent's left or right child, updates the child's parent pointer, and updates the parent node's height.
AVLTreeSetChild(parent, whichChild, child) {
if (whichChild != "left" && whichChild != "right")
return False
if (whichChild == "left")
parent→left = child
else
parent→right = child
if (child != null)
child→parent = parent
AVLTreeUpdateHeight(parent)
return true
}
The AVLTreeReplaceChild algorithm replaces one of a node's existing child pointers with a new value, utilizing AVLTreeSetChild to perform the replacement.
AVLTreeReplaceChild(parent, currentChild, newChild) {
if (parent→left == currentChild)
return AVLTreeSetChild(parent, "left", newChild)
else if (parent→right == currentChild)
return AVLTreeSetChild(parent, "right", newChild)
return false
}
The AVLTreeGetBalance algorithm computes a node's balance factor by subtracting the right subtree height from the left subtree height.
AVLTreeGetBalance(node) {
leftHeight = -1
if (node→left != null)
leftHeight = node→left→height
rightHeight = -1
if (node→right != null)
rightHeight = node→right→height
return leftHeight - rightHeight
}
Now let's check out the actual algorithm of rotations with the corresponding pseudocodes!
Right Rotation Algorithm
A right rotation algorithm is defined on a subtree root (node D) which must have a left child (node B).
The algorithm reassigns child pointers, assigning B's right child with D, and assigning D's left child with C (B's original right child, which may be null)
If D's parent is non-null, the parent's child D is replaced with B.
Other tree parts (T1...T4 below) naturally stay with their parent nodes.

AVLTreeRotateRight(tree, node) {
leftRightChild = node→left→right
if (node→parent != null)
AVLTreeReplaceChild(node→parent, node, node→left)
else { # node is root
tree→root = node→left
tree→root→parent = null
}
AVLTreeSetChild(node→left, "right", node)
AVLTreeSetChild(node, "left", leftRightChild)
}
Okay then exactly when should we perform left/right rotation, and how do we know?
We want to balance the tree when an AVL tree node has a balance factor of 2 or -2, which only occurs after an insertion or removal, the node must be rebalanced via rotations.
The AVLTree Balance algorithm updates the height value at a node, computes the balance factor, and rotates if the balance factor is 2 or -2.
AVLTreeRebalance(tree, node) {
AVLTreeUpdateHeight(node)
if (AVLTreeGetBalance(node) == -2) {
if (AVLTreeGetBalance(node→right) == 1) {
# Double Rotation Case
AVLTreeRotateRight(tree, node→right)
}
return AVLTreeRotateLeft(tree, node)
}
else if (AVLTreeGetBalance(node) == 2) {
if (AVLTreeGetBalance(node→left) == -1) {
# Double rotation case
AVLTreeRotateLeft(tree, node→left)
}
return AVLTreeRotateRight(tree, node)
}
return node
}'Data Science > Data Structure & Algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Data Structure] Red-Black Tree - 1 (0) | 2025.05.02 |
|---|---|
| [Data Structure] AVL Tree - 3: AVL Insertions & Removals (0) | 2025.05.01 |
| [Data Structure] AVL Tree - 1: Introduction (0) | 2025.05.01 |
| [Data Structure] Python: Binary Search Tree (0) | 2025.04.23 |
| [Data Structure] BST Parent Node Pointers, and Recursion (0) | 2025.04.23 |



